Overview
Background
The architecture of Linkis0.X mainly has the following problems
- The boundary between the core processing flow and the hierarchical module is blurred:
Entrance and EngineManager function boundaries are blurred.
The main process of task submission and execution is not clear enough.
It is troublesome to extend the new engine, and it needs to implement the code of multiple modules.
Only support computing request scenarios, storage request scenarios and resident service mode (Cluster) are difficult to support.
- Demands for richer and more powerful computing governance functions:
Insufficient support for computing task management strategies.
The labeling capability is not strong enough, which restricts computing strategies and resource managemen.
The new architecture of Linkis1.0 computing governance service can solve these problems well.
Architecture Diagram
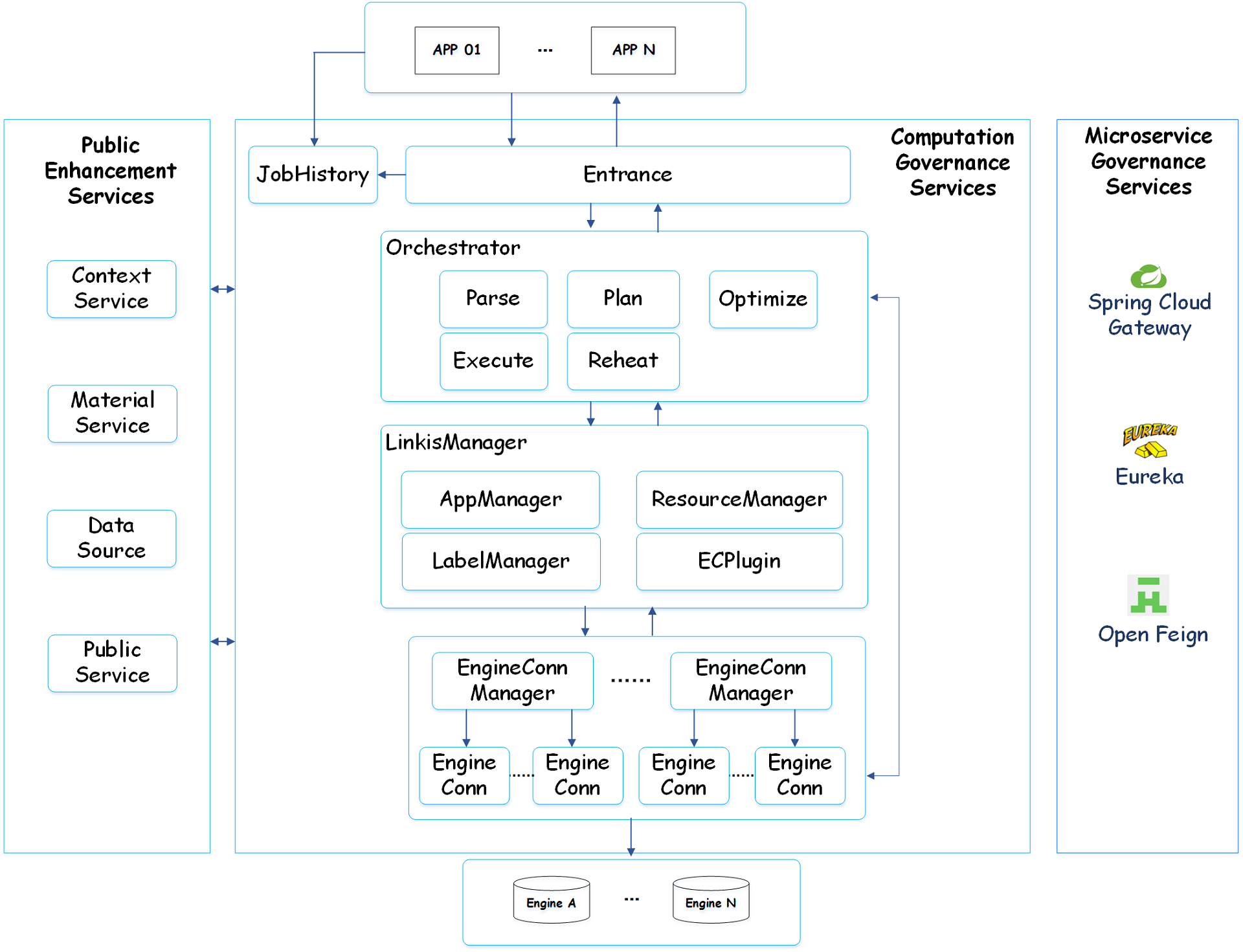
Operation process optimization: Linkis1.0 will optimize the overall execution process of the job, from submission —> preparation —>
Perform three stages to fully upgrade Linkis's Job execution architecture, as shown in the following figure:

Architecture Description
1. Entrance
Entrance, as the submission portal for computing tasks, provides task reception, scheduling and job information forwarding capabilities. It is a native capability split from Linkis0.X's Entrance.
Entrance Architecture Design
2. Orchestrator
Orchestrator, as the entrance to the preparation phase, inherits the capabilities of parsing Jobs, applying for Engines, and submitting execution from Entrance of Linkis0.X; at the same time, Orchestrator will provide powerful orchestration and computing strategy capabilities to meet multiple activities, active backups, transactions, and replays. , Current limiting, heterogeneous and mixed computing and other application scenarios.
3. LinkisManager
As the management brain of Linkis, LinkisManager is mainly composed of AppManager, ResourceManager, LabelManager and EngineConnPlugin.
- ResourceManager not only has Linkis0.X's resource management capabilities for Yarn and Linkis EngineManager, but also provides tag-based multi-level resource allocation and recycling capabilities, allowing ResourceManager to have full resource management capabilities across clusters and across computing resource types;
- AppManager will coordinate and manage all EngineConnManager and EngineConn. The life cycle of EngineConn application, reuse, creation, switching, and destruction will be handed over to AppManager for management; and LabelManager will provide cross-IDC and cross-cluster based on multi-level combined tags EngineConn and EngineConnManager routing and management capabilities;
- EngineConnPlugin is mainly used to reduce the access cost of new computing storage, so that users can access a new computing storage engine only by implementing one class.
Enter LinkisManager Architecture Design
4. Engine Manager
Engine conn Manager (ECM) is a simplified and upgraded version of linkis0. X engine manager. The ECM under linkis1.0 removes the application ability of the engine, and the whole microservice is completely stateless. It will focus on supporting the startup and destruction of all kinds of enginecon.
Enter EngineConnManager Architecture Design
5. EngineConn
EngineConn is an optimized and upgraded version of Linkis0.X Engine. It will provide EngineConn and Executor two modules. EngineConn is used to connect the underlying computing storage engine and provide a session session that connects the underlying computing storage engines; Executor is based on this Session session , Provide full-stack computing support for interactive computing, streaming computing, offline computing, and data storage.
Enter EngineConn Architecture Design