Hive Engine
1 Use of Hive Engine
The Hive execution engine implemented by Linkis now supports HiveQL submission, and users submit their own execution through Linkis using the three interface methods in the document (SDK, HTTP, WebSocket) Code, you can submit your HiveQL to the cluster for execution.
If you want to use the Linkis system to execute the HiveQL program, you need to download the Linkis release installation package and configure, install and start the specified specified microservice.
1.1 Environment variable configuration
Environmental variables that the Hive engine depends on: HADOOP_HOME, HADOOP_CONF_DIR, HIVE_HOME, and HIVE_CONF_DIR.
Before starting the microservices related to the hive execution engine, please make sure that the above environment variables have been set. If not, please log in /home/${ USER}/.bash_rc or linkis-ujes-spark-enginemanager/conf in the linkis.properties configuration file. As shown below
HADOOP_HOME=${real hadoop installation directory}
HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${Real hadoop configuration directory}
HIVE_CONF_DIR=${Real hive configuration directory}
HIVE_HOME=${Real hive installation directory}
1.2 Dependent service startup
The startup of the Hive engine requires the following Linkis microservices:
-1), Eureka: Used for service registration and discovery. -2), Linkis-gateway: used for user request forwarding. -3) Linkis-publicService: Provides basic functions such as persistence and udf. -4) Linkis-ResourceManager: Provides Linkis resource management functions.
1.3 Custom parameter configuration
To use hive normally, you also need to start HiveEntrance and HiveEngineManager.
HiveEntrance is the recipient of hive jobs, and HiveEngineManager is the initiator of HiveEngine.
Before starting, users can set custom parameters about the hive engine.
Linkis provides many configuration parameters in consideration of users' desire to set parameters more freely.
The following table has some commonly used parameters. The Hive engine supports configuring more parameters for better performance. If you have tuning needs, welcome to read Tuning manual.
Users can configure these parameters in linkis.properties.
| Parameter name | Reference value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wds.linkis.enginemanager.memory.max | 40G | Used to specify the total memory of the client of all engines started by hiveEM |
| wds.linkis.enginemanager.cores.max | 20 | Used to specify the total number of CPU cores of the clients of all engines started by hiveEM |
| wds.linkis.enginemanager.engine.instances.max | 10 | Used to specify the number of engines that hiveEM can start |
1.4 Front-end deployment
After the above microservices are successfully launched and deployed, users need to submit their own HiveQL code through a web browser. You can deploy another open source front-end product of WeBank [Scriptis](https://github.com/WeBankFinTech/Scriptis/blob/master/docs/zh_CN/ch1/%E5%89%8D%E5%8F% B0%E9%83%A8%E7%BD%B2%E6%96%87%E6%A1%A3.md), this product allows users to edit and submit codes on web pages, and receive real-time feedback from the background information.
1.5 Running effect chart
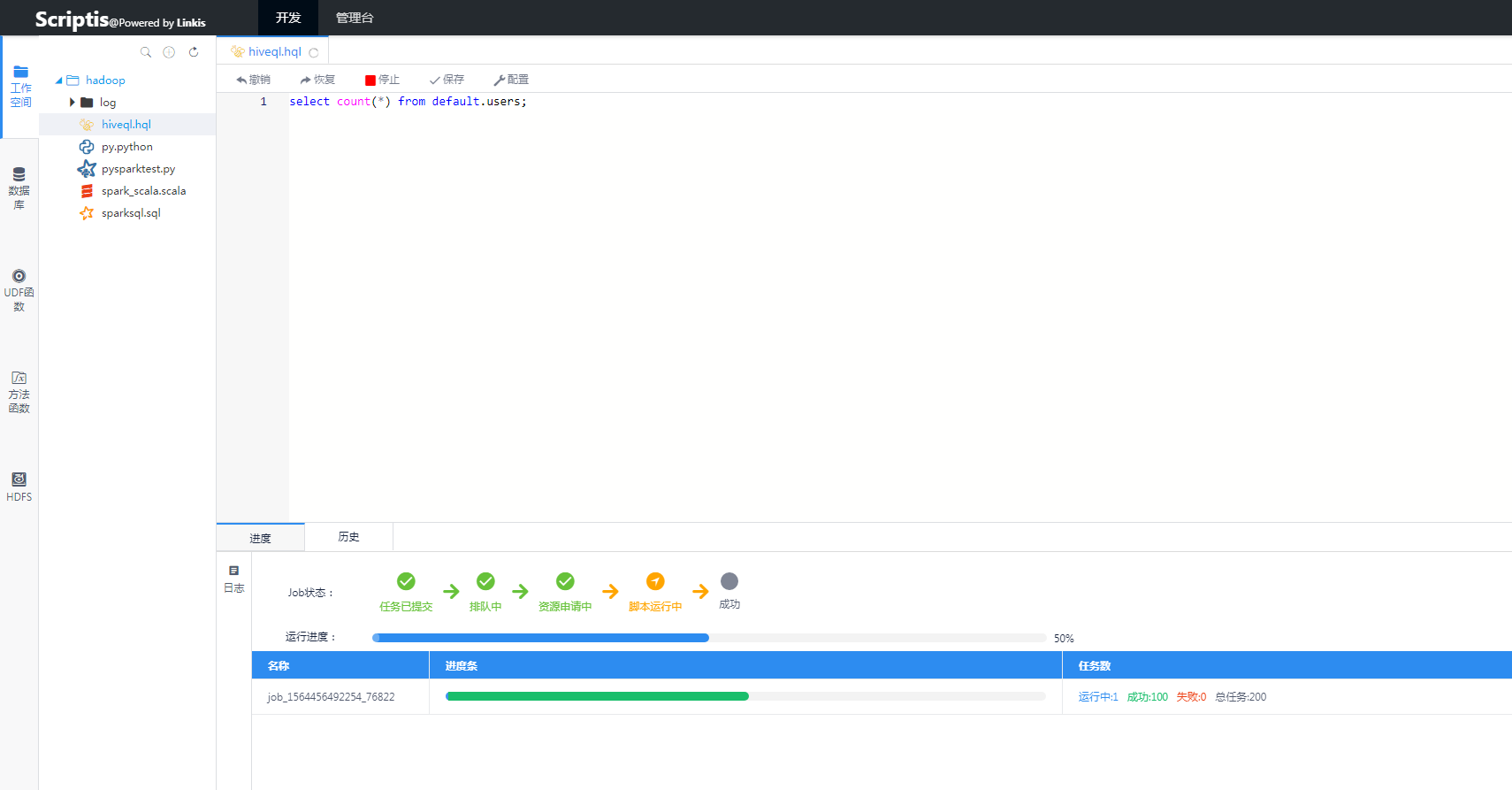
Figure 1 Hive running effect Figure 1
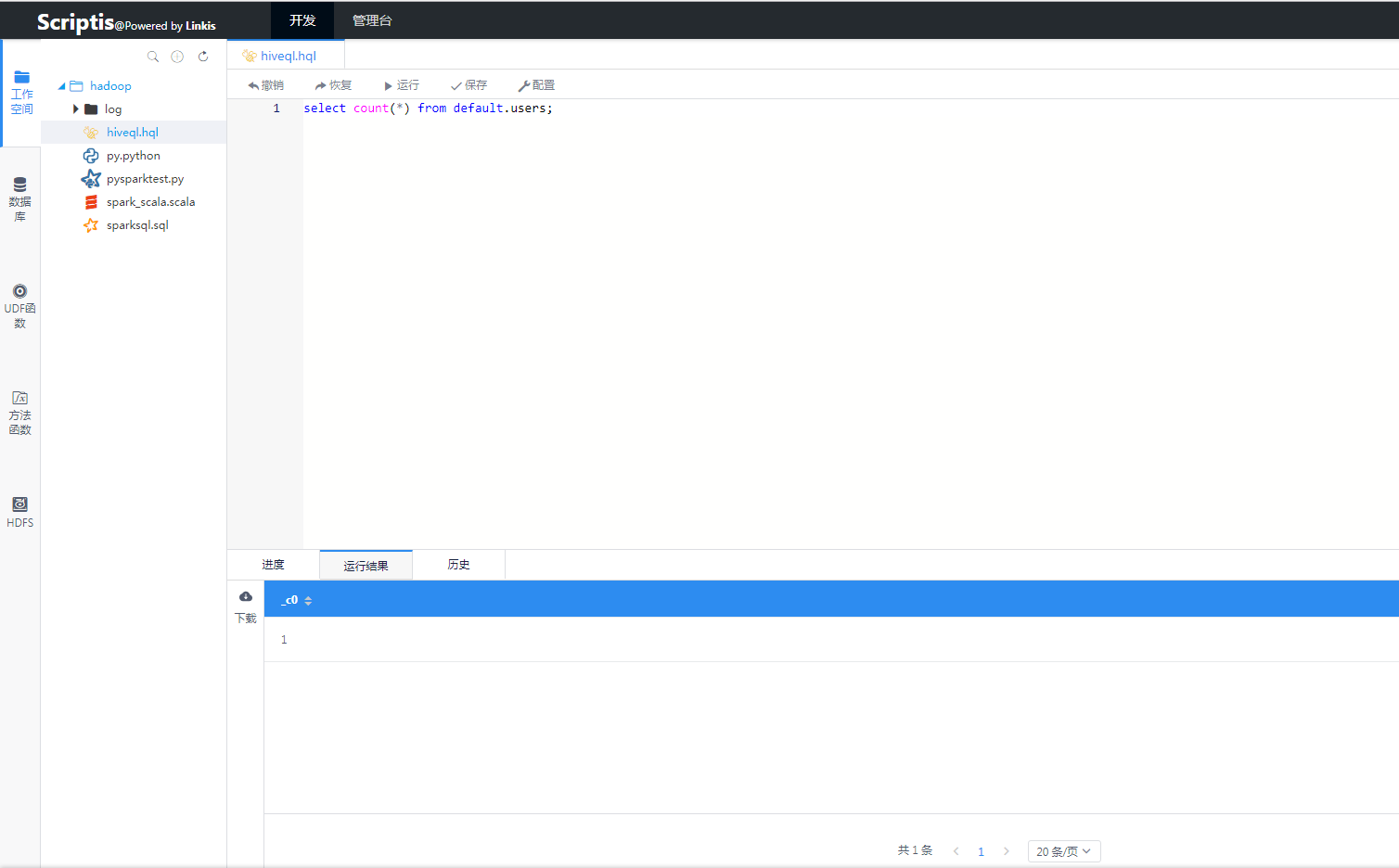
Figure 2 Hive running effect Figure 2
2 Hive engine implementation
The implementation of the Hive execution engine is to implement the necessary interfaces of the Entrance, EngineManager and Engine three modules with reference to the Linkis development document. The Engine module is the most special, Hive The way of implementation also has its own set of logic.
The Release version now provided by Linkis is based on hadoop version 2.7.2, hive version is 1.2.1, both are apache versions.
Linkis's Hive engine interacts with the underlying hive mainly through the HiveEngineExecutor class, which is instantiated by the HiveEngineExecutorFactory bean.
In the executeLine interface implemented by HiveEngineExecutor, Linkis uses the CommandProcessorFactory class provided by hive to pass in local hive configuration information to obtain an org.apache.hadoop. The hive.ql.Driver class, the Driver class provides an API to help submit the user's script code to the cluster for execution.
After the driver submits the hive sql code, there is an API to provide whether the execution is successful and to obtain the result set after the success is obtained. If the execution is successful, with the help of the unified storage service provided by Linkis, the result set will be stored in the specified directory for users to view.
In addition, after the Driver submits hive sql, if a mapreduce task is generated, we can also kill the submitted hive query task through the killRunningJobs API provided by HadoopJobExecHelper , This is the logic of the user's foreground kill task.
One more thing, Linkis's hive engine also implements a progress function. Specifically, the runningJobs field of HadoopJobExecHelper is used to obtain the running MR tasks, and then these MR tasks have corresponding map and reduce progress. You can get the total progress of the task by doing a mathematical calculation. It should be noted that runningJobs is running The MR job will be deleted from the List once it is executed, so it is necessary to get the execution plan of SQL at the beginning. For details, please refer to the implementation of the code.
3 Adapt your own hive version
Because the current version of Linkis is the apache version that supports 1.2.1, many users' clusters may not be consistent with our company, so you need to recompile the Hive execution engine by yourself .
For example, if the user is using the 1.1.0 cdh version, he needs to change the hive.version to the specified version in the top-level pom.xml and then Compile.
When we were adapting, we also found that there was a conflict in the jar package. This requires the user to check the log to eliminate it. If the cause is still unclear, welcome to join the group for consultation.

4 Future goals
- Seamlessly adapt to more hive versions.
- The deployment method is simpler, try to use the containerized method.
- The function is more complete, and it is more accurate and complete in terms of execution progress, data accuracy, etc.