WebSocket Request
Gateway's multi-WebSocket request forward implementation
1 feature point
Frontend Client and Background WebSocket Microservice more than 1 N support
WebSocket Channel All Life Cycle Management
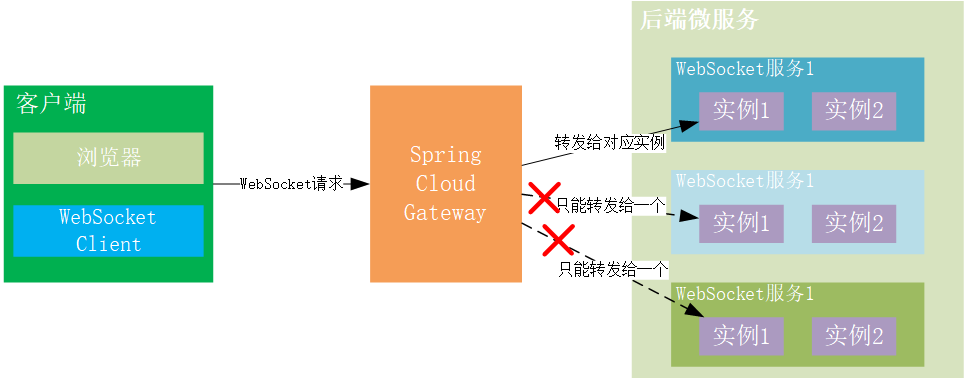
2 Zuul's Bug
Forward WebSocket request is not supported at all.
3 Spring Cloud Gateway Limitations
A WebSocket client can only forward the request to a specific background service and cannot complete a WebSocket client via the gateway API to multiple WebSocket microservices.
4 Linkis Solution
Linkis implemented in Spring Cloud Gateway in WebSocket router transponder to set up WebSocket connections with clients and automatically analyze client WebSocket requests and pass rules to which backend microservice the request is forwarded to the corresponding backend service instance.
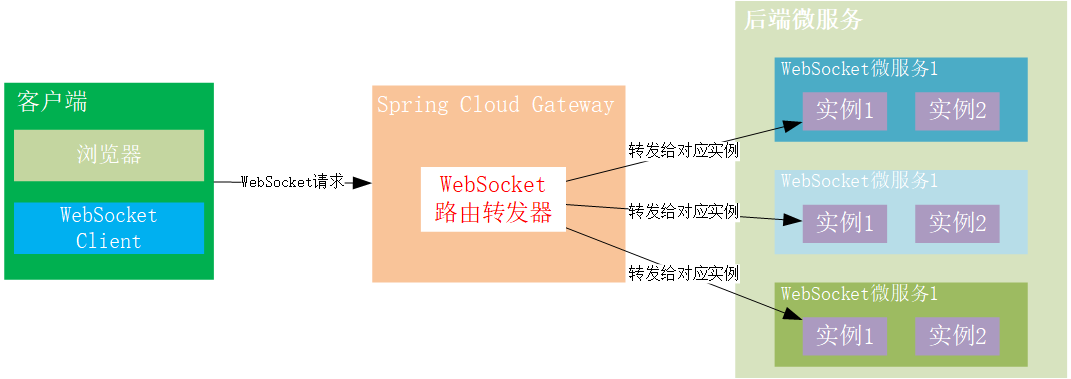
WebSocket router transponder to build up WebSocket requests for clients, down to multiple WebSocket microservice instances for back-end backenders. In order to implement WebSocket request based on rules to forward clients, the architecture of WebSocket router transponder is:
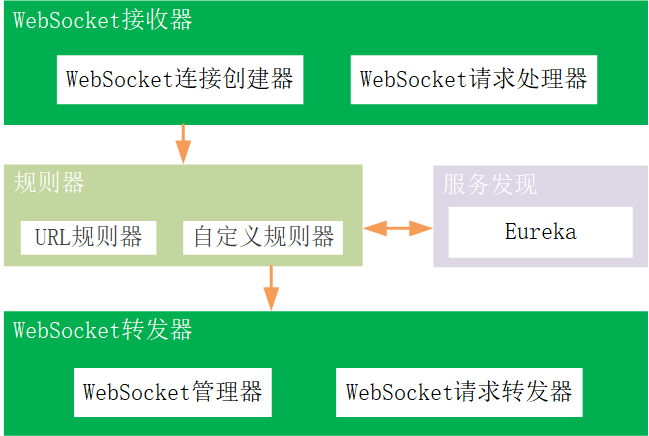
4.1 WebSocket Receiver
1) WebSocket receiver is a global filter for Spring Cloud Gateway, which receives client's WebSocket connection request and creates a 1-WebSocket channel for client communication with Spring Cloud Gateway.
2) At the same time, it listens to the WebSocket channel, sends clients to send incoming requests, obtain essential basic information (such as requests to addresses, uri and users), provide a simple encapsulation and pass to the rulers for processing.
4.2 Rulers
1) Rulers receive a notification from WebSocket Recipient, start processing using rules
2) URL Ruler
Linkis defines the client's requested text frame (TextWebSocketFrame) as a JSON string for the following:
"{'method': '/api/v1/${service}/${uriPath}', 'data': '}"
where:
This method is the actual request URI, the previous /api fixed as an API request, v1 refers to the version of the API, service is the name of the requested service, uriPath is the actual request URI.
Data is actual requested data.
Get service information by parsing method, pass to step 4.
3) If the client requests a text frame (TextWebSocketFrame) does not conform to the standard format of the URL Ruler or if the URL Ruler cannot parse service information, then load the user-defined rule to parse service. If all custom rulers cannot parse service messages, then a solution error will be dropped to the client directly; otherwise service information will be passed to the next step directly
4) Access to service information by step 2 or step 3, when the ruler obtains a list of all healthy microservices from the discovery service (e.g. Eureka), finds all examples of the microservice and selects one of the smallest payload instance to the WebSocket transponder by means of a load equilibrium approach.
4.3 WebSocket transponder
The WebSocket Forwarders are distributed as WebSocket Manager and WebSocket Request Forwarder.
1) WebSocket Manager
The WebSocket Manager is responsible for managing the 1-to-1WebSocket connection channel between clients and WebSocket receivers, and the 1-to-multiWebSocket connection channel between WebSocket transponder and backend microservice instances.
If the client disconnects with WebSocket receiver, the WebSocket Manager will immediately disconnect all related WebSocket transponders from the backend microservice instance by 1 to/multi-WebSocket;
At the same time, in order to keep all WebSocket transponders and backend microservice instances from being freed for being idle, the WebSocket Manager will always send the backend microservice instance for PingWebSocketFrame.
2) WebSocket Request Rotor
WebSocket Request Forwarders get microservice instance information from the Ruler
Here you need to take note of the distinction between service and service instances:a microservice has multiple instances. Each instance has exactly the same functionality.
Seek from the WebSocket Manager for the client and the microservice service if there is already a WebSocket transponder to the WebSocket connection channel of the microservice and, if it exists, use the webSocket connection channel to forward the client's request text frame (TextWebSocketFrame); otherwise, create a completely new webSocket connection for the client and this microservice instance and bind the new WebSocket connection and the client to the WebSocket receiver 1 for the 1 WebSocket connection to the web Socket, and then push the information back to the client via the link between the client and the WebSocket receiver.